Data Structures and Algorithms Part I
Last Modified: 4/10/2025
2 Linked Lists
A linked list is a linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, each element points to the next.
In the implementation we use a sentinel code. Sentinel code make it easier to reason about code, and also give you specific goals to strive for in making sure your code works.
2.1 Singly Linked List
Singly linked lists contain nodes which have a value field as well as next field, which points to the next node in line of nodes.
97 collapsed lines
import java.util.Iterator;
public class SLList<T> implements Iterable<T> {
/** * Node class for SLList */ public static class Node<T> { public T item; public Node<T> next;
public Node(T i, Node<T> n) { item = i; next = n; } }
private final Node<T> sentinel; private int size;
/** * Default Constructor for SLList */ public SLList() { sentinel = new Node<>(null, null); size = 0; }
/** * Constructor for SLList with one element * * @param x element to be added */ public SLList(T x) { sentinel = new Node<>(null, null); sentinel.next = new Node<>(x, null); size = 1; }
/** * Add element to the front of the list * * @param x element to be added */ public void addFirst(T x) { sentinel.next = new Node<>(x, sentinel.next); size += 1; }
/** * Add element to the end of the list * * @param x element to be added */ public void addLast(T x) { size += 1; Node<T> p = sentinel; while (p.next != null) { p = p.next; } p.next = new Node<>(x, null); }
/** * Return the size of the list * * @return size of the list */ public int size() { return size; }
/** * Iterator implementation for SLList */ public Iterator<T> iterator() { return new SLListIterator(); }
private class SLListIterator implements Iterator<T> { private Node<T> p;
public SLListIterator() { p = sentinel.next; }
public boolean hasNext() { return p != null; }
public T next() { T returnItem = p.item; p = p.next; return returnItem; } }}132 collapsed lines
#ifndef SLLIST_H#define SLLIST_H
#include <iterator>
template <typename T>class SLList {public: template <typename U> struct Node { U item; Node* next;
Node(U i, Node<U>* n) : item(i), next(n) {} };
private: Node<T>* sentinel; int size;
public: SLList(); explicit SLList(T x); void addFirst(T x); void addLast(T x); [[nodiscard]] int getSize() const; class iterator; iterator begin(); iterator end();};
template <typename T>class SLList<T>::iterator {public: using iterator_category = std::forward_iterator_tag; using value_type = T; using difference_type = std::ptrdiff_t; using pointer = T*; using reference = T&;
private: Node<T>* current;
public: explicit iterator(Node<T>* node) : current(node) {} T& operator*() const; T* operator->() const; iterator& operator++(); bool operator==(const iterator& other) const; bool operator!=(const iterator& other) const;};
template <typename T>SLList<T>::SLList() : sentinel(new Node<T>(T(), nullptr)), size(0) {}
template <typename T>SLList<T>::SLList(T x) : sentinel(new Node<T>(T(), nullptr)), size(1) { sentinel->next = new Node<T>(x, nullptr);}
/** * Add element to the front of the list */template <typename T>void SLList<T>::addFirst(T x) { sentinel->next = new Node<T>(x, sentinel->next); size++;}
/** * Add element to the end of the list */template <typename T>void SLList<T>::addLast(T x) { size++; Node<T>* p = sentinel; while (p->next != nullptr) { p = p->next; } p->next = new Node<T>(x, nullptr);}
/** * Return the size of the list */template <typename T>int SLList<T>::getSize() const { return size;}
/** * Iterator implementation for SLList */template <typename T>typename SLList<T>::iterator SLList<T>::begin() { return iterator(sentinel->next);}
template <typename T>typename SLList<T>::iterator SLList<T>::end() { return iterator(nullptr);}
template <typename T>T& SLList<T>::iterator::operator*() const { return current->item;}
template <typename T>T* SLList<T>::iterator::operator->() const { return &(current->item);}
template <typename T>typename SLList<T>::iterator& SLList<T>::iterator::operator++() { if (current) { current = current->next; } return *this;}
template <typename T>bool SLList<T>::iterator::operator==(const iterator& other) const { return current == other.current;}
template <typename T>bool SLList<T>::iterator::operator!=(const iterator& other) const { return !(*this == other);}
#endif // SLLIST_H45 collapsed lines
class Node: """Represents a node in the singly linked list.""" def __init__(self, item, next_node): """Initializes a Node with an item and the next node.""" self.item = item self.next = next_node
class SLList: """Represents a singly linked list.""" def __init__(self, x=None): """ Initializes an SLList. If x is provided, initializes the list with one element x. Uses a sentinel node at the front. """ self.sentinel = Node(None, None) self.size_val = 0
if x is not None: self.sentinel.next = Node(x, None) self.size_val = 1
def add_first(self, item): """Adds an item to the front of the list.""" self.sentinel.next = Node(item, self.sentinel.next) self.size_val += 1
def add_last(self, item): """Adds an item to the end of the list.""" self.size_val += 1 p = self.sentinel while p.next is not None: p = p.next p.next = Node(item, None)
def size(self): """Returns the number of items in the list.""" return self.size_val
def __iter__(self): """Returns an iterator for the SLList.""" p = self.sentinel.next while p is not None: yield p.item p = p.next2.2 Doubly Linked List
While a deque defines the behavior (an interface) of a double-ended queue, a doubly linked list provides one way to realize that behavior through its design.
111 collapsed lines
import java.util.Iterator;
public class DLList<T> implements Iterable<T> {
/** * Node class for DLList. * Each node holds a reference to its item and pointers to the previous and next * nodes. */ private static class Node<T> { public T item; public Node<T> prev; public Node<T> next;
public Node(T item, Node<T> prev, Node<T> next) { this.item = item; this.prev = prev; this.next = next; } }
private final Node<T> sentinel; private int size;
/** * Default constructor for an empty DLList. * A circular sentinel node is created where sentinel.next and sentinel.prev point to sentinel itself. */ public DLList() { sentinel = new Node<>(null, null, null); sentinel.next = sentinel; sentinel.prev = sentinel; size = 0; }
/** * Constructor for DLList with one element. * * @param x the element to be added */ public DLList(T x) { sentinel = new Node<>(null, null, null); Node<T> newNode = new Node<>(x, sentinel, sentinel); sentinel.next = newNode; sentinel.prev = newNode; size = 1; }
/** * Adds an element to the front of the list. * * @param x the element to be added */ public void addFirst(T x) { Node<T> newNode = new Node<>(x, sentinel, sentinel.next); sentinel.next.prev = newNode; sentinel.next = newNode; size++; }
/** * Adds an element to the end of the list. * * @param x the element to be added */ public void addLast(T x) { Node<T> newNode = new Node<>(x, sentinel.prev, sentinel); sentinel.prev.next = newNode; sentinel.prev = newNode; size++; }
/** * Returns the size of the list. * * @return the number of elements in the list */ public int size() { return size; }
/** * Provides an iterator over the list's elements. * * @return an iterator that traverses the list from front to back */ @Override public Iterator<T> iterator() { return new DLListIterator(); }
private class DLListIterator implements Iterator<T> { private Node<T> current;
public DLListIterator() { current = sentinel.next; }
@Override public boolean hasNext() { return current != sentinel; }
@Override public T next() { T returnItem = current.item; current = current.next; return returnItem; } }}156 collapsed lines
#ifndef DLLIST_H#define DLLIST_H
#include <iterator>#include <cstddef>
template <typename T>class DLList {public: template <typename U> struct Node { U item; Node* next; Node* prev;
Node(U i, Node<U>* p, Node<U>* n) : item(i), next(n), prev(p) {} };
private: Node<T>* sentinel; int size;
public: DLList(); explicit DLList(T x); void addFirst(T x); void addLast(T x); [[nodiscard]] int getSize() const; class iterator; iterator begin(); iterator end();};
template <typename T>class DLList<T>::iterator {public: using iterator_category = std::bidirectional_iterator_tag; using value_type = T; using difference_type = std::ptrdiff_t; using pointer = T*; using reference = T&;
private: Node<T>* current;
public: explicit iterator(Node<T>* node) : current(node) {}
T& operator*() const; T* operator->() const; iterator& operator++(); iterator& operator--(); bool operator==(const iterator& other) const; bool operator!=(const iterator& other) const;};
/************************************** * Implementation of the DLList class.* **************************************/
/* Default constructor: creates an empty list with a circular sentinel node. */template <typename T>DLList<T>::DLList() : size(0) { sentinel = new Node<T>(T(), nullptr, nullptr); sentinel->next = sentinel; sentinel->prev = sentinel;}
/* Constructor with one element. */template <typename T>DLList<T>::DLList(T x) : size(1) { sentinel = new Node<T>(T(), nullptr, nullptr); sentinel->next = sentinel; sentinel->prev = sentinel; auto* newNode = new Node<T>(x, sentinel, sentinel); sentinel->next = newNode; sentinel->prev = newNode; newNode->next = sentinel; newNode->prev = sentinel;}
/* Add element to the front of the list. */template <typename T>void DLList<T>::addFirst(T x) { auto* newNode = new Node<T>(x, sentinel, sentinel->next); sentinel->next->prev = newNode; sentinel->next = newNode; size++;}
/* Add element to the end of the list. */template <typename T>void DLList<T>::addLast(T x) { auto* newNode = new Node<T>(x, sentinel->prev, sentinel); sentinel->prev->next = newNode; sentinel->prev = newNode; size++;}
/* Return the size of the list. */template <typename T>int DLList<T>::getSize() const { return size;}
/* Returns iterator to the first element. */template <typename T>typename DLList<T>::iterator DLList<T>::begin() { return iterator(sentinel->next);}
/* Returns iterator to the end (sentinel node). */template <typename T>typename DLList<T>::iterator DLList<T>::end() { return iterator(sentinel);}
/*************************** * Iterator Implementation * ***************************/
template <typename T>T& DLList<T>::iterator::operator*() const { return current->item;}
template <typename T>T* DLList<T>::iterator::operator->() const { return &(current->item);}
/* Pre-increment: move to the next node. */template <typename T>typename DLList<T>::iterator& DLList<T>::iterator::operator++() { current = current->next; return *this;}
/* Pre-decrement: move to the previous node. */template <typename T>typename DLList<T>::iterator& DLList<T>::iterator::operator--() { current = current->prev; return *this;}
template <typename T>bool DLList<T>::iterator::operator==(const iterator& other) const { return current == other.current;}
template <typename T>bool DLList<T>::iterator::operator!=(const iterator& other) const { return !(*this == other);}
#endif // DLLIST_H45 collapsed lines
class DLList: class Node: def __init__(self, item, prev=None, next=None): self.item = item self.prev = prev self.next = next
def __init__(self): # Create a circular sentinel node. self.sentinel = self.Node(None) self.sentinel.next = self.sentinel self.sentinel.prev = self.sentinel self.size = 0
def addFirst(self, x): """Add an element to the front of the list.""" new_node = self.Node(x, self.sentinel, self.sentinel.next) self.sentinel.next.prev = new_node self.sentinel.next = new_node self.size += 1
def addLast(self, x): """Add an element to the end of the list.""" new_node = self.Node(x, self.sentinel.prev, self.sentinel) self.sentinel.prev.next = new_node self.sentinel.prev = new_node self.size += 1
def getSize(self): """Return the size of the list.""" return self.size
def __iter__(self): """Forward iterator: iterate from the first element to the end.""" current = self.sentinel.next while current != self.sentinel: yield current.item current = current.next
def iter_backward(self): """Backward iterator: iterate from the last element to the beginning.""" current = self.sentinel.prev while current != self.sentinel: yield current.item current = current.prev3 Union-Find (Disjoint Sets)
Union-Find data structure (also known as Disjoint-Set data structure), is a data structure that stores a collection of disjoint (non-overlapping) sets. It provides operations for adding new sets, merging sets (replacing them with their union), and finding a representative member of a set.
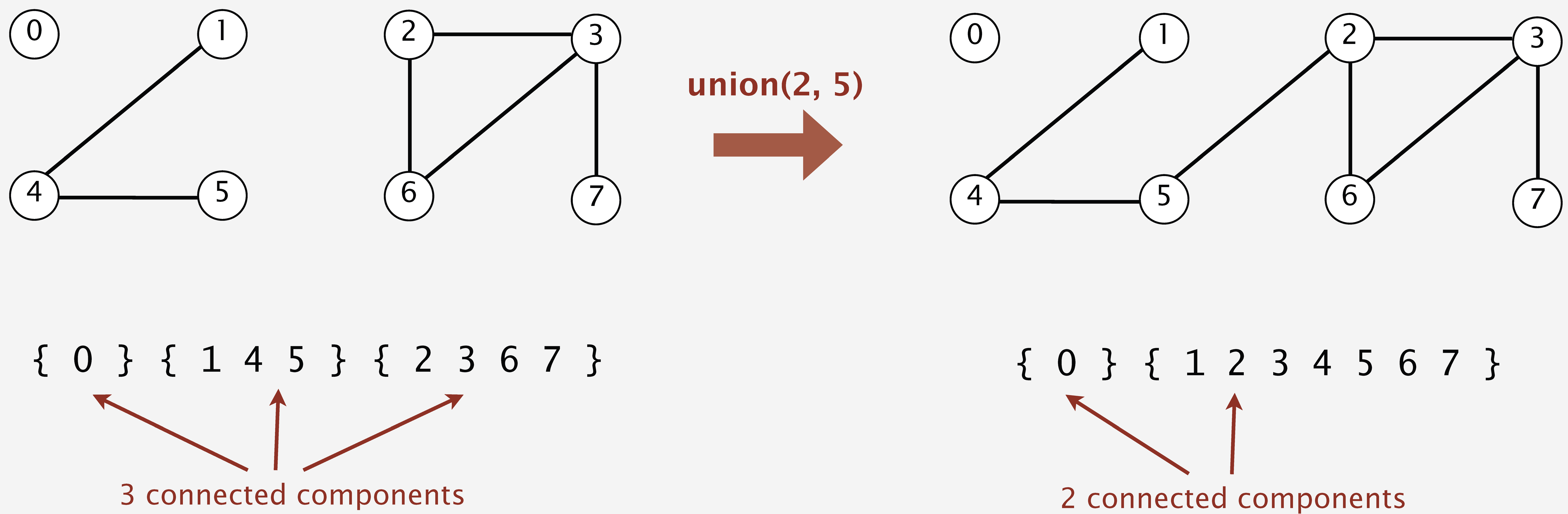
3.1 Quick Find (Eager Approach)
parent[i]is the root of , and are connected if and only if they have the sameparent[i].- Find: Check if and have the same
parent[i]. - Union: To merge components containing and , change all entries whose id equals
parent[p]toparent[q].
3.2 Quick Union (Lazy Approach)
parent[i]is the parent of , root of isparent[parent...[i]](keep going until it doesn’t change)- Find: Check if and have the same root.
- Union: To merge components containing and , set the id of ‘s root to the id of ‘s root.
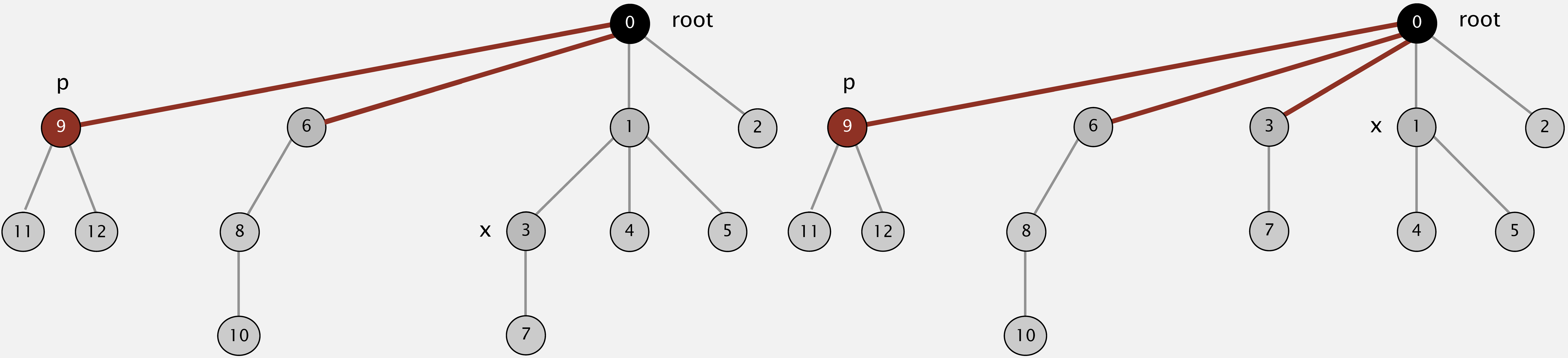
3.3 Quick Union Improvements
For quick union, we can improve the algorithm by using weighted quick union and path compression (WQUPC).
- Weighted quick-union: Keep track of size of each tree (number of objects), and balance it by linking root of smaller tree to root of larger tree, so that trees won’t be too tall.
- Path compression: Change the pointer of this node to skip a level, closer to the root or directly point at the root. In this way, the tree will get flatter.
Propositions
-
Depth of any node is at most
Proof:
The depth of increase by when tree containing is merged into another tree . The size of the tree containing at least doubles since .
Therefore, the size of tree containing can double at most times.
-
Starting from an empty data structure, any sequence of union-find ops on objects makes array accesses.
The amortized time for any
findorunionoperations on a disjoint-set forest containing objects is , where denotes the iterated logarithm. -
In theory, WQUPC is not quite linear, but in practice, it is linear.
In “cell-probe” model of computation, no linear-algorithm exists.
84 collapsed lines
import java.util.Scanner;
public class UF {
private final int[] parent; // parent[i] = parent of i private final byte[] rank; // rank[i] = rank of subtree rooted at i (never more than 31) private int count; // number of components
/** * Initializes an empty union-find data structure with * {@code n} elements 0 through n-1. * Initially, each element is in its own set. * * @param n the number of elements * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code n < 0} */ public UF(int n) { if (n < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("n must be non-negative"); count = n; parent = new int[n]; rank = new byte[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { parent[i] = i; rank[i] = 0; } }
/** * Returns the canonical element (root) of the set containing element p. * * @param p an element * @return the canonical element of the set containing p * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless 0 <= p < n */ public int find(int p) { validate(p); while (p != parent[p]) { parent[p] = parent[parent[p]]; // path compression p = parent[p]; } return p; }
/** * Returns the number of sets. * * @return the number of sets (between 1 and n) */ public int count() { return count; }
/** * Merges the set containing element p with the set containing element q. * * @param p one element * @param q the other element * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless 0 <= p < n and 0 <= q < n */ public void union(int p, int q) { int rootP = find(p); int rootQ = find(q); if (rootP == rootQ) return;
/* Weighted Quick Union: Make root of smaller rank point to root of larger rank. */ if (rank[rootP] < rank[rootQ]) { parent[rootP] = rootQ; } else if (rank[rootP] > rank[rootQ]) { parent[rootQ] = rootP; } else { parent[rootQ] = rootP; rank[rootP]++; } count--; }
// Validates that p is a valid index. private void validate(int p) { int n = parent.length; if (p < 0 || p >= n) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (n - 1)); } }}96 collapsed lines
#ifndef UF_H#define UF_H
#include <vector>#include <stdexcept>#include <string>
/** * @brief The UnionFind class represents a union–find data type (disjoint sets). * * This implementation uses weighted quick union by rank with * path compression by halving. * * @tparam T The type used for indices (default is int). */template <typename T = int>class UnionFind {private: std::vector<T> parent; // parent[i] = parent of i std::vector<int> rank; // rank[i] = rank of subtree rooted at i int count; // number of components
// Validate that p is a valid index. void validate(T p) const { if (p < 0 || p >= static_cast<T>(parent.size())) throw std::out_of_range("Index " + std::to_string(p) + " is not between 0 and " + std::to_string(parent.size() - 1)); }
public: /** * @brief Constructs a union-find structure with n elements 0 ... n-1. * * @param n the number of elements * @throws std::invalid_argument if n is negative */ explicit UnionFind(int n) : parent(n), rank(n, 0), count(n) { if (n < 0) throw std::invalid_argument("n must be non-negative"); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) parent[i] = static_cast<T>(i); }
/** * @brief Finds the canonical element (root) of the set containing p. * * Uses path compression by halving. * * @param p an element * @return the root of the set containing p * @throws std::out_of_range if p is not a valid index */ T find(T p) { validate(p); while (p != parent[p]) { parent[p] = parent[parent[p]]; // path compression p = parent[p]; } return p; }
/** * @brief Merges the set containing element p with the set containing element q. * * @param p one element * @param q another element */ void unionSets(T p, T q) { T rootP = find(p); T rootQ = find(q); if (rootP == rootQ) return;
/* Weighted Quick Union: Make the tree with smaller rank point to the one with larger rank. */ if (rank[rootP] < rank[rootQ]) parent[rootP] = rootQ; else if (rank[rootP] > rank[rootQ]) parent[rootQ] = rootP; else { parent[rootQ] = rootP; ++rank[rootP]; } --count; }
/** * @brief Returns the number of disjoint sets. * * @return the number of connected components */ [[nodiscard]] int countSets() const { return count; }};
#endif // UF_H66 collapsed lines
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n): """ Initializes an empty union-find data structure with n elements 0 through n-1. Each element is initially in its own set. :param n: the number of elements (must be non-negative) :raises ValueError: if n is negative """ if n < 0: raise ValueError("n must be non-negative") self.count = n self.parent = list(range(n)) self.rank = [0] * n
def _validate(self, p): """ Validates that p is a valid index. :param p: an element index :raises ValueError: if p is not between 0 and n-1 """ n = len(self.parent) if p < 0 or p >= n: raise ValueError(f"Index {p} is not between 0 and {n - 1}")
def find(self, p): """ Returns the canonical element (root) of the set containing p. Implements path compression by halving. :param p: an element :return: the root of the set containing p """ self._validate(p) while p != self.parent[p]: self.parent[p] = self.parent[self.parent[p]] # path compression p = self.parent[p] return p
def union(self, p, q): """ Merges the set containing element p with the set containing element q. :param p: one element :param q: another element """ rootp = self.find(p) rootq = self.find(q) if rootp == rootq: return
# Make the tree with smaller rank point to the tree with larger rank. if self.rank[rootp] < self.rank[rootq]: self.parent[rootp] = rootq elif self.rank[rootp] > self.rank[rootq]: self.parent[rootq] = rootp else: self.parent[rootq] = rootp self.rank[rootp] += 1
self.count -= 1
def count_sets(self): """ Returns the number of disjoint sets. :return: number of connected components """ return self.countApplications: Percoloation, games, dynamic connectivity, least common ancestor, Kruskal’s minimum spanning tree algorithm, etc.