Artificial Intelligence
Last Modified: 4/10/2025
1 Searching
1.1 Agent Design
There are mainly two types of agents: reflex agents and planning agents.
-
Reflex Agents
- Choose action based on current percept, and may have memory or a model of the world’s current state.
- Do not consider the future consequences of their actions, just consider how the world IS.
-
Planning Agents
- Decisions based on (hypothesized) consequences of actions.
- Must have a model of how the world evolves in response to actions, and formulate a goal (test), consider how the world WOULD BE.
1.2 Search Problems & Algorithms
A search problem consists of a state space, a successor function (with actions and costs), a start space and a goal test. A solution is a sequence of actions (a plan) which transforms the start state to a goal state.
For a search problem, we may need:
- State Space Graph: A mathematical representation of a search problem. It consists of nodes (abstarcted world configurations) and arcs (successors/action results). The goal test is a set of goal nodes (maybe only one).
- *Search Trees: A “what if” tree of plans and their outcomes. Nodes show states, and children correspond to successors.
Search algorithms can be divided into two categories:
- Uninformed Search: No additional information about states beyond the definition of the problem.
- Depth-First Search
- Breadth-First Search
- Uniform-Cost Search
- Informed Search: Use heuristics to guide the search.
- A* Search
1.2.1 Uniform-Cost Search
Uniform-cost search is a variant of Dijkstra’s algorithm. Not inserting all nodes in a graph makes it possible to extend Dijkstra’s algorithm to find the shortest path from a single source to the closest of a set of target nodes on infinite graphs or those too large to represent in memory, which is called uniform-cost search (UCS) in artificial intelligence literature.
105 collapsed lines
import java.util.*;
public class UCS<T> { private final Map<T, Double> costTo; private final Map<T, T> parent; private final PriorityQueue<T> pq; private final Set<T> visited;
/** * A directed edge constructor with a cost. */ public static class Edge<T> { T neighbor; double cost;
public Edge(T neighbor, double cost) { this.neighbor = neighbor; this.cost = cost; } }
/** * Uniform-cost search constructor. */ public UCS(Map<T, List<Edge<T>>> graph, T startNode) { costTo = new HashMap<>(); parent = new HashMap<>(); visited = new HashSet<>();
for (T node : graph.keySet()) { costTo.put(node, Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY); parent.put(node, null); } costTo.put(startNode, 0.0);
pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingDouble(costTo::get)); pq.offer(startNode);
while (!pq.isEmpty()) { T currentNode = pq.poll(); visited.add(currentNode);
if (costTo.get(currentNode) == Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY) continue;
for (Edge<T> edge : graph.get(currentNode)) { relax(currentNode, edge.neighbor, edge.cost); } } }
/** * Relaxation of an edge. * * @param u the source node * @param v the target node * @param cost the cost of the edge */ private void relax(T u, T v, double cost) { if (costTo.get(v) > costTo.get(u) + cost) { costTo.put(v, costTo.get(u) + cost); parent.put(v, u); pq.offer(v); } }
/** * Get the cost to a node. * * @param node the target node * @return the cost to the target node */ public double getCostTo(T node) { return costTo.getOrDefault(node, Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY); }
/** * Check if a path exists to a node. * * @param node the target node * @return true if a path exists, false otherwise */ public boolean hasPathTo(T node) { return costTo.get(node) < Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; }
/** * Get the path to a node. * * @param targetNode the target node * @return the path to the target node */ public List<T> getPathTo(T targetNode) { if (!hasPathTo(targetNode)) { return null; }
List<T> path = new ArrayList<>(); for (T v = targetNode; v != null; v = parent.get(v)) { path.add(v); }
Collections.reverse(path); return path; }}88 collapsed lines
#ifndef UCS_H#define UCS_H
#include <unordered_map>#include <unordered_set>#include <vector>#include <queue>#include <limits>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>
template <typename T>class UCS {public: struct Edge { T neighbor; double cost;
Edge(T neighbor, const double cost) : neighbor(neighbor), cost(cost) {} };
private: std::unordered_map<T, double> costTo; std::unordered_map<T, T> parent; std::priority_queue<T, std::vector<T>, std::function<bool(T, T)>> pq; std::unordered_set<T> visited;
public: UCS(const std::unordered_map<T, std::vector<Edge>>& graph, const T& startNode) : pq([this](T a, T b) { return costTo[a] > costTo[b]; }) {
for (const auto& node : graph) { costTo[node.first] = std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity(); parent[node.first] = T(); } costTo[startNode] = 0.0;
pq.push(startNode);
while (!pq.empty()) { T currentNode = pq.top(); pq.pop(); visited.insert(currentNode);
if (costTo[currentNode] == std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity()) continue;
for (const auto& edge : graph.at(currentNode)) { relax(currentNode, edge.neighbor, edge.cost); } } }
void relax(const T& u, const T& v, double cost) { if (costTo[v] > costTo[u] + cost) { costTo[v] = costTo[u] + cost; parent[v] = u; pq.push(v); } }
double getCostTo(const T& node) const { auto it = costTo.find(node); if (it != costTo.end()) { return it->second; } return std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity(); }
bool hasPathTo(const T& node) const { return getCostTo(node) < std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity(); }
std::vector<T> getPathTo(const T& targetNode) const { if (!hasPathTo(targetNode)) { return {}; }
std::vector<T> path; for (T v = targetNode; v != T(); v = parent.at(v)) { path.push_back(v); }
std::reverse(path.begin(), path.end()); return path; }};
#endif // UCS_H85 collapsed lines
class Edge: def __init__(self, neighbor, cost): """ An edge with a neighbor and a cost. """ self.neighbor = neighbor self.cost = cost
class UCS: def __init__(self, graph, start_node): """ Initialize uniform-cost search with a graph and a start node. 'graph' is a dict mapping each node to a list of Edge objects. """ self.cost_to = {} self.parent = {} self.visited = set() self.adj = graph
# Initialize all costs to infinity and parents to None for node in graph: self.cost_to[node] = float('inf') self.parent[node] = None
# Start node cost is 0 self.cost_to[start_node] = 0.0
# Use a list for priority queue (heapq) instead of PriorityQueue import heapq self.pq = [] heapq.heappush(self.pq, (0.0, start_node))
# Main loop while self.pq: current_cost, current_node = heapq.heappop(self.pq) if current_node in self.visited: continue
self.visited.add(current_node)
# Skip if unreachable if self.cost_to[current_node] == float('inf'): continue
# Relax edges of current node for edge in self.adj.get(current_node, []): self.relax(current_node, edge.neighbor, edge.cost)
def relax(self, u, v, cost): """ Update cost_to[v] (relaxation) if a cheaper path is found. """ new_cost = self.cost_to[u] + cost if new_cost < self.cost_to[v]: self.cost_to[v] = new_cost self.parent[v] = u import heapq heapq.heappush(self.pq, (new_cost, v))
def get_cost_to(self, node): """ Get the cost of the path to 'node'. """ return self.cost_to.get(node, float('inf'))
def has_path_to(self, node): """ Check if a path to 'node' exists. """ return self.get_cost_to(node) < float('inf')
def get_path_to(self, target_node): """ Reconstruct the path to 'target_node'. Returns None if no path exists. """ if not self.has_path_to(target_node): return None
path = [] current = target_node while current is not None: path.append(current) current = self.parent[current] return path[::-1]1.2.2 A* Search
A* search is a kind of heuristic search algorithms. It combines uniform-cost search and greedy algorithm.
- : The cost of the path from the start node to , which uniform-cost search relies on (path cost).
- : A heuristic function that estimates the cost of the cheapest path from to the goal, which greedy algorithm relies on (goal proximity).
The A* search algorithm uses the following formula to calculate the cost of a node:
A heuristic is admissible (optimistic) if:
where is the true cost to reach the goal from node .
The admissible heuristic guarantees that A* will never stop exploring a path that could lead to a better solution. With inadmissible heuristics, A* may think a node is “too expensive” and stop exploring it, even if that node is actually on the optimal path.
For admissible heuristics, there are some methods for calculating :
- Manhattan Distance: The sum of the absolute differences of the and coordinates.
- Euclidean Distance: The straight-line distance between two points.
- Chebyshev Distance: The maximum of the absolute differences of the and coordinates.
- Octile Distance: The diagonal distance between two points.
- Zero Heuristic: The heuristic that always returns zero, which makes it the same as uniform-cost search.
Properties
-
Admissibility: A search algorithm is said to be admissible if it is guaranteed to return an optimal solution. If the heuristic function used by A* is admissible, then A* is admissible.
-
Consistency: The estimate of heuristic function is always less than or equal to the estimated distance from any neighbouring vertex to the goal, plus the cost of reaching that neighbour.
where is the cost from to . In other words, heuristic “arc” cost less than the actual cost for each arc.
Consistency ensures that the estimated total cost is non-decreasing along any path. This means once A* expands a node, the cost found for that node is the lowest possible, and the node will not need to be re-expanded later. It leads to more efficient searches.
For tree search, A* is optimal if heuristic is admissible; for graph search, A* is optimal if heuristic is consistent. In general, most natural admissible heuristics tend to be consistent, especially if from relaxed problems.
- Completeness: On finite graphs with non-negative edge weights A* is guaranteed to terminate and is complete, i.e. it will always find a solution (a path from start to goal) if one exists.
99 collapsed lines
import java.util.*;
public class AStarSearch { public static class Node implements Comparable<Node> { int x, y; double f, g, h; Node parent;
public Node(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
@Override public int compareTo(Node other) { return Double.compare(this.f, other.f); }
@Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (!(obj instanceof Node other)) return false; return this.x == other.x && this.y == other.y; }
@Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(x, y); } }
private static boolean isValid(int[][] grid, int x, int y) { return (x >= 0 && x < grid.length && y >= 0 && y < grid[0].length && grid[x][y] == 0); }
// Manhattan distance private static double heuristic(Node a, Node b) { return Math.abs(a.x - b.x) + Math.abs(a.y - b.y); }
public static List<Node> aStar(int[][] grid, Node start, Node goal) { PriorityQueue<Node> openSet = new PriorityQueue<>(); Set<Node> closedSet = new HashSet<>();
start.g = 0; start.h = heuristic(start, goal); start.f = start.g + start.h; openSet.add(start);
while (!openSet.isEmpty()) { Node current = openSet.poll();
if (current.equals(goal)) { return reconstructPath(current); }
closedSet.add(current);
int[][] directions = { {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0} }; for (int[] dir : directions) { int newX = current.x + dir[0]; int newY = current.y + dir[1]; if (!isValid(grid, newX, newY)) continue;
Node neighbor = new Node(newX, newY); if (closedSet.contains(neighbor)) continue;
double tentativeG = current.g + 1;
boolean inOpenSet = openSet.contains(neighbor); if (!inOpenSet || tentativeG < neighbor.g) { neighbor.parent = current; neighbor.g = tentativeG; neighbor.h = heuristic(neighbor, goal); neighbor.f = neighbor.g + neighbor.h;
if (!inOpenSet) { openSet.add(neighbor); } } } } return null; }
private static List<Node> reconstructPath(Node current) { List<Node> path = new ArrayList<>(); while (current != null) { path.add(current); current = current.parent; } Collections.reverse(path); return path; }}113 collapsed lines
#ifndef ASTARSEARCH_H#define ASTARSEARCH_H
#include <vector>#include <queue>#include <cmath>#include <algorithm>#include <utility>
struct Node { int x, y; double f, g, h; Node* parent;
Node(const int x, const int y) : x(x), y(y), f(0), g(0), h(0), parent(nullptr) {}
bool operator==(const Node& other) const { return x == other.x && y == other.y; }};
struct CompareNode { bool operator()(const Node* a, const Node* b) const { return a->f > b->f; }};
namespace AStar { // Manhattan distance heuristic inline double heuristic(const Node* a, const Node* b) { return std::abs(a->x - b->x) + std::abs(a->y - b->y); }
// Check if cell (x, y) is valid and walkable in the grid inline bool isValid(const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& grid, int x, int y) { return (x >= 0 && x < grid.size() && y >= 0 && y < grid[0].size() && grid[x][y] == 0); }
// Reconstruct the path from goal to start by following parent pointers. inline std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> reconstructPath(Node* current) { std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> path; while (current != nullptr) { path.emplace_back(current->x, current->y); current = current->parent; } std::ranges::reverse(path); return path; }
// A* search algorithm. // Note: For simplicity, this example does not free allocated memory. inline std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> aStar(const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& grid, Node* start, const Node* goal) { std::priority_queue<Node*, std::vector<Node*>, CompareNode> openSet; std::vector<Node*> closedSet;
start->g = 0; start->h = heuristic(start, goal); start->f = start->g + start->h; openSet.push(start);
constexpr int directions[4][2] = { {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0} };
while (!openSet.empty()) { Node* current = openSet.top(); openSet.pop();
// Goal check if (*current == *goal) { return reconstructPath(current); }
closedSet.push_back(current);
// Explore neighbors for (const auto direction : directions) { const int newX = current->x + direction[0]; const int newY = current->y + direction[1];
if (!isValid(grid, newX, newY)) continue;
auto neighbor = new Node(newX, newY);
// Skip if neighbor is in closedSet bool skip = false; for (const Node* closedNode : closedSet) { if (*closedNode == *neighbor) { skip = true; break; } } if (skip) { delete neighbor; continue; }
const double tentativeG = current->g + 1;
neighbor->parent = current; neighbor->g = tentativeG; neighbor->h = heuristic(neighbor, goal); neighbor->f = neighbor->g + neighbor->h; openSet.push(neighbor); } }
return {}; }}
#endif // ASTARSEARCH_H84 collapsed lines
import heapq
class Node: def __init__(self, x, y): self.x = x self.y = y self.f = 0.0 self.g = 0.0 self.h = 0.0 self.parent = None
def __lt__(self, other): return self.f < other.f
def __eq__(self, other): if other is None: return False return self.x == other.x and self.y == other.y
def __hash__(self): return hash((self.x, self.y))
def is_valid(grid, x, y): return (0 <= x < len(grid) and 0 <= y < len(grid[0]) and grid[x][y] == 0)
def heuristic(a, b): return abs(a.x - b.x) + abs(a.y - b.y)
def a_star(grid, start, goal): open_set = [] closed_set = set()
start.g = 0 start.h = heuristic(start, goal) start.f = start.g + start.h heapq.heappush(open_set, (start.f, start))
while open_set: current_f, current_node = heapq.heappop(open_set) if current_node == goal: return reconstruct_path(current_node)
closed_set.add(current_node)
directions = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0)] for dir_x, dir_y in directions: new_x = current_node.x + dir_x new_y = current_node.y + dir_y if not is_valid(grid, new_x, new_y): continue
neighbor = Node(new_x, new_y) if neighbor in closed_set: continue
tentative_g = current_node.g + 1
in_open_set = False for _, node_in_open_set in open_set: if node_in_open_set == neighbor: in_open_set = True break
if not in_open_set or tentative_g < neighbor.g: neighbor.parent = current_node neighbor.g = tentative_g neighbor.h = heuristic(neighbor, goal) neighbor.f = neighbor.g + neighbor.h
if not in_open_set: heapq.heappush(open_set, (neighbor.f, neighbor)) else: pass
return None
def reconstruct_path(current_node): path = [] while current_node: path.append(current_node) current_node = current_node.parent return path[::-1]1.3 Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs)
Constraint satisfaction problems (CSPs) are mathematical questions defined as a set of objects whose state must satisfy a number of constraints or limitations. In CSPs, state is defined by variables with values froma domain , and the goal test is a set of constraints specifying allowable combinations of values for subsets of variables.
For example, for the map coloring problem below,
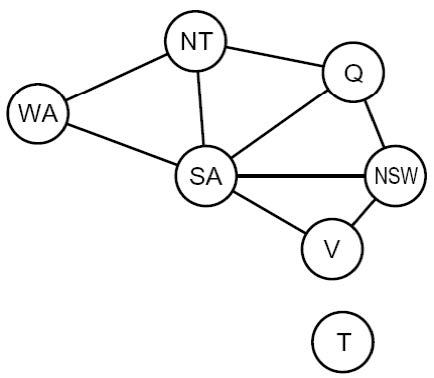
1.3.1 Varieties of CSPs and Constraints
Varieties of CSPs
-
Discrete Variables:
- Finite domains: e.g., map coloring.
- Infinite domains: e.g., job scheduling, variables are start/end times for each job.
- Continuous Variables: e.g., start/end times for Hubble Telescope observations.
Varieties of Constraints
- Unary constraints involve a single variable (e.g., ).
- Binary constraints involve pairs of variables (e.g., ).
- Higher-order constraints involve three or more variables (e.g., cryptarithmetic column constraints).
1.3.2 Backtracking Search
Backtracking is a class of algorithms that incrementally builds candidates to the solutions, and abandons a candidate (“backtracks”) as soon as it determines that the candidate cannot possibly be completed to a valid solution. This is based on the idea of depth-first search, with two more improvements:
- Pruning (Check constraints as you go): If a partial assignment violates a constraint, we can prune the search space by not considering any extensions of that assignment. E.g., if and , we can prune any assignment of that is equal to 1.
- Filtering (Forward checking): If a variable is assigned, we can remove any inconsistent values from the domains of the remaining unassigned variables. E.g., if and , we can directly remove 1 from the domain of when we assign instead of waiting until we assign .